Technology
FAQ
| Biological Computing | |
|
| Molecular Biology - Genetics | |
|
| Bioinformatics | |
Modern molecular biology would be impossible without computer technology. The huge amount of data makes the use of computers for analysis, storage and retrieval obligatory. Bio computing covers a wide range of information processing, including mathematical modelling, statistical models, graphical user interfaces, simulation, databases and many more. Standard problems in biocomputing are genome rearrangement, gene finding or protein folding. Bioinformatics practical is an online course in biocomputing Questions:
|
| Biotechnologyne | |
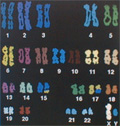
Men have at all times wondered about the nature of heredity. Around the 18th century botanists began experimenting with plant crossing in a systematic way. The concept of a gene was introduced by Gregor Mendel in 1866. Since then we have learned a lot about the influence genes have on the characteristics of a certain species or an individual creature. Biotechnology seeks to exploit this knowledge for the development of new products or improving existing ones. Current biotechnology methods, which allow the transfer of a gene from one organism to another, involve the same basic scientific processes (crossbreeding and fermentation) people have used for in the past to increase crop productivity. (see GM Food)
|